President Trump’s Tax Return


If one might say, the news of the year (or even four years), has been what we read on Sunday, September 27, 2020, “New York Times: Trump Paid No Income Taxes in 10 out of 15 years beginning 2020.” The report stated that in both the year he won the presidency and his first year in the White House, Trump paid just $750 in federal income taxes.
Trump denied the New York Times story and claimed that he pays “a lot” in federal and state income taxes, as was expected.
“Tax bombshell reveals Trump’s image as a sham” read CNN story. The CNN story further stated that “In 2016 and 2017 each, Trump paid just $750 in federal income taxes — far less than many Americans who are working hard amid a deep recession to stay afloat.”
Here are a few pieces of general knowledge about Income tax in USA:
Passed by Congress on July 2, 1909, and ratified February 3, 1913, the 16th Amendment established Congress’ right to impose a Federal income tax.
The history of Income tax in USA, however, goes back to 1861. During the Civil War Congress passed the Revenue Act of 1861 which included a tax on personal incomes to help pay war expenses. The tax was repealed ten years later. However, in 1894 Congress enacted a flat rate Federal income tax, which was ruled unconstitutional the following year by the U.S. Supreme Court because it was a direct tax not apportioned according to the population of each state. The 16th amendment, ratified in 1913, removed this objection by allowing the Federal government to tax the income of individuals without regard to the population of each State.(www.loc.gov)
Incidentally, the rate of tax, during1861-1871, was 3% of all incomes over US$800.
As of 2019, “About 50 percent of federal revenue comes from individual income taxes, 7 percent from corporate income taxes, and another 36 percent from payroll taxes that fund social insurance programs (figure 1). The rest comes from a mix of sources”, writes Tax Policy Center.
It will not be out of place to state that social insurance (payroll) tax is effectively an earmarked revenue, meaning it will, by and large, go to a predetermined use.
The unearmarked tax revenue is thus only 64%.
Each of the other tax category expressed as a percentage of unearmarked federal revenue will read as follows:
| Individual Income Tax | 78.12% |
| Corporate Income Tax | 10.94% |
| Excise and Others | 12.50 |
| Based on numbers provided by Tax Policy Center. Rounding off Error 1.56 per cent points. |
Clearly, Individual Income Tax contributes the real big chunk of federal revenue. Corporate Income tax is the second best bet to raise money by taxes.
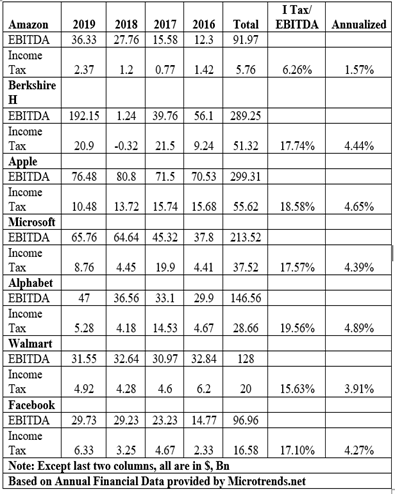
The table given at the end shows that select leading corporations of USA pay corporate income tax at an average rate in the range of 1.57% to 4.89%, per year.
Important Notes:
A few other interesting facts:
President Trump’s tax return debate should be used to review the current system of income tax in USA. If USA could move to a flat rate or expenditure tax instead of income tax, the productivity of average American will certainly shoot up.
Dr Sat Parashar, PhD is former Director, IIM Indore. He teaches at University of California, San Diego, and is a Financial Services Professional. He may be reached at writetospp@gmail.com
DISCLAIMER: The author is solely responsible for the views expressed in this article. The author carries the responsibility for citing and/or licensing of images utilized within the text.
